Intranasal esketamine in the management of treatment-resistant depression in a patient with a history of emotional neglect in childhood
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.25118/2763-9037.2024.v14.1201Keywords:
Esketamine, Depressive Disorder, Treatment-Resistant, Child Abuse, Suicide, Attempted, ketamine, TRDAbstract
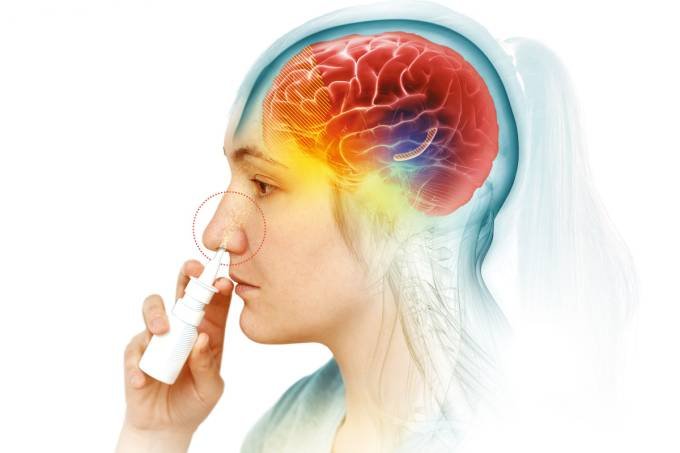
Introduction: Emotional neglect in childhood is a recognized risk factor for the development of Treatment-Resistant Depression (TRD) in adulthood. This case presents the association between emotional neglect in childhood, failure of conventional antidepressants, and partial success with intranasal esketamine associated with antidepressant in the treatment of TRD. Method: Case report. CAAE 82360424.6.0000.0082, Faculdade de Medicina do ABC, FMABC. Case Presentation: A 29-year-old woman, with a history of emotional neglect in childhood, started with a depressive episode at 15 years old. After treatment failures with conventional antidepressants, she was diagnosed with TRD and underwent therapy with intranasal esketamine associated with desvenlafaxine, resulting in partial improvement of depressive symptoms. Discussion: The clinical history highlights the association between emotional neglect in childhood and the development of TRD in adulthood. The lack of response to conventional antidepressants underscores the challenges faced in the treatment of TRD. Intranasal esketamine associated with desvenlafaxine has proven to be a promising therapeutic approach for cases of TRD, offering a treatment perspective. Conclusions: It emphasizes the importance of recognizing and addressing emotional neglect in childhood as a risk factor for TRD and the need to explore alternative therapeutic options, such as intranasal esketamine associated with antidepressants, for patients who do not respond to conventional antidepressants.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Teicher MH, Samson JA, Anderson CM, Ohashi K. The effects of childhood maltreatment on brain structure, function and connectivity. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2016;17(10):652-666. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2016.111 - PMid:27640984 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2016.111
Felitti VJ, Anda RF, Nordenberg D, Williamson DF, Spitz AM, Edwards V, Marks JS. Relationship of childhood abuse and household dysfunction to many of the leading causes of death in adults: The Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) Study. American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 1998;14(4), 245-258. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0749-3797(98)00017-8 - PMid:9635069 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0749-3797(98)00017-8
Green JG, McLaughlin KA, Berglund PA, Gruber MJ, Sampson NA, Zaslavsky AM, Kessler RC. Childhood adversities and adult psychiatric disorders in the national comorbidity survey replication I: associations with first onset of DSM-IV disorders. Archives of general psychiatry. 2010;67(2):113-123. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.186 PMid:20124111 PMCid:PMC2822662 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.186
Norman RE, Byambaa M, De R, Butchart A, Scott J, Vos T. The long-term health consequences of child physical abuse, emotional abuse, and neglect: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS medicine. 2012;9(11):e1001349. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001349 - PMid:23209385 PMCid:PMC3507962 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001349
Juruena MF. Early-life stress and HPA axis trigger recurrent adulthood depression. Epilepsy Behav. 2014;38:148-59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2013.10.020 - PMid:24269030 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2013.10.020
Martins-Monteverde CMS, Baes CVW, Reisdorfer E, Padovan T, Tofoli SMC, Juruena MF. Relationship between depression and subtypes of early life stress in adult psychiatric patients. Front Psychiatry. 2019;10:19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00019 PMid:30804815 - PMCid:PMC6370718 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00019
Teicher M, De Souza CLM, Wang H, Juruena M, Raskin MA, Kaye RF. The emotional maltreatment and neglect questionnaire (EMNQ): a one-year follow-up of a community sample of 12-18-year-old youths. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2021;295:420-426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2021.06.061 - PMid:34256182 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2021.06.061
Juruena MF. Early life stress, depression and epigenetics. Vitam Horm. 2023;122:307-337. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.vh.2023.01.004 - PMid:36863799 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.vh.2023.01.004
Sackeim HA. The definition and meaning of treatment-resistant depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;62,Suppl 16:10-7. https://doi.org/10.4088/jcp.v62n0102 - PMid:11235934 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.v62n0102
Daly EJ, Trivedi MH, Janik A, Li H, Zhang Y, Li X, Hellerstein DJ. Efficacy and safety of esketamine nasal spray plus oral antidepressant treatment for relapse prevention in patients with treatment-resistant depression: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(9):893-903. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.1189 PMid:31166571 PMCid:PMC6551577 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.1189
Charlson F, van Ommeren M, Flaxman A, Cornett J, Whiteford H, Saxena S. New WHO prevalence estimates of mental disorders in conflict settings: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet [online]. 2019;394(10194):240-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(19)30934-1 - PMid:31200992 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30934-1
Popova V, Daly EJ, Trivedi M, Cooper K, Lane R, Lim P, Mazzucco C, Hough D, Thase ME, Shelton RC, Molero P, Vieta E, Bajbouj M, Manji H, Drevets WC, Singh JB. Efficacy and safety of flexibly dosed esketamine nasal spray combined with a newly initiated oral antidepressant in treatment-resistant depression: a randomized double-blind active-controlled study. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176(6):428-38. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2019.19020172 - PMid:31109201 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2019.19020172
Zarate CA, Singh JB, Carlson PJ, Brutsche NE, Ameli R, Luckenbaugh DA, Charney DS, Manji HK. A randomized trial of an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Archives of General Psychiatry[online]. 2006;63(8):856. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.63.8.856 - PMid:16894061 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.63.8.856
Bahji A, Vázquez GH, Zarate CA. Comparative efficacy of racemic ketamine and esketamine for depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2020;278:12473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2020.09.071 PMid:33022440 - PMCid:PMC7704936 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2020.09.071
Young AH, Abdelghani M, Juruena MF, Nikolova VL, Nilforooshan R. Early clinical experiences of esketamine nasal spray in the UK in adults with treatment-resistant major depressive disorder: advisory panel recommendations. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023;19:433-441. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S388392 - PMid:36861011 PMCid:PMC9968662 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S388392
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 César Augusto Trinta Weber, Cintia de Azevedo-Marques Périco, Flávia Ismael Pinto

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Debates em Psiquiatria allows the author (s) to keep their copyrights unrestricted. Allows the author (s) to retain their publication rights without restriction. Authors should ensure that the article is an original work without fabrication, fraud or plagiarism; does not infringe any copyright or right of ownership of any third party. Authors should also ensure that each one complies with the authorship requirements as recommended by the ICMJE and understand that if the article or part of it is flawed or fraudulent, each author shares responsibility.
Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) - Debates em Psiquiatria is governed by the licencse CC-By-NC
You are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material
The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms. Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.




























